Kano Model
Easily visualize and explain the impact and priority of different features
Val Yonchev
What Is Kano Model?
The Kano model is derived from the work of professor Noriaki Kano on product development and customer satisfaction.
Why Do Kano Model?
- The Kano Model is widely used in Product Management for prioritisation of product features. It allows for easy visualisation and explanation of the impact and priority of different features.
- It can involve the whole product team in the decision-making and help increase transparency of product decisions.
- Developing new products goes hand in hand with generation of ideas, hypothesis and their testing/validation. Unfortunately, it is mostly impossible to test and evaluate all ideas and hypothesis we can come up with, which requires us to filter and prioritize work on them.
- It is a simple, easy to understand and very visual and can include the whole team in the process of transparent selection of ideas/hypothesis to work on first.
- Helps the Product Managers (Product Owners) in prioritisation, building the product roadmap/backlog and explaining priorities to stakeholders.
- It helps identify directions and ideas for pivoting.
How to do Kano Model?
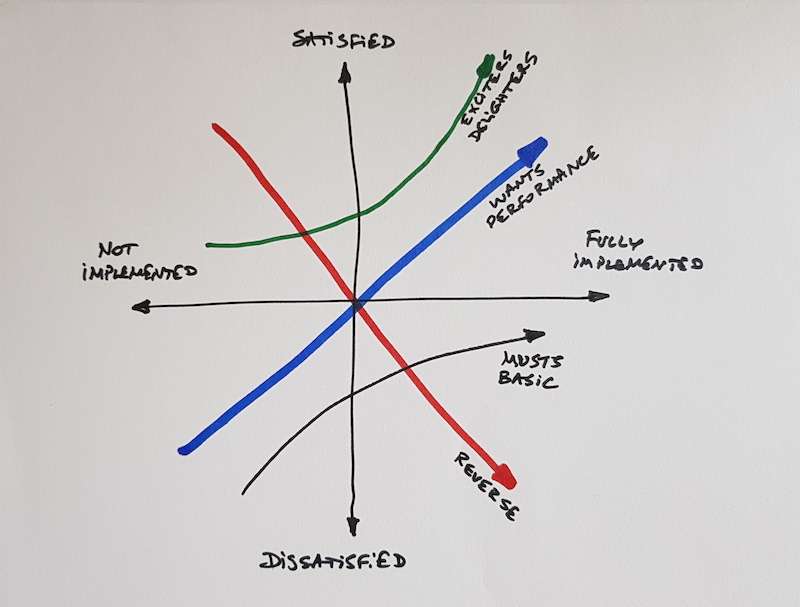
Prof. Kano argues that customer preferences can be classified in five categories:
Must Have / Must-be (aka Musts, Basic Needs, Dissatisfiers) - covers product/feature expectations (requirements) which are taken for granted by the customers. When done well, customers are neutral, when not present or done poorly customers are very disappointed
One dimensional (aka Wants, Satisfiers, Wow factors) - covers product/feature expectations which are leading to satisfaction when present and dissatisfaction when not present
Attractive (aka Delighters)- covers product/feature expectations which provide satisfaction when realised, but do NOT cause dissatisfaction if not present
Indifferent (aka Neutrals) - covers product/feature expectations which are neither good nor bad in terms of impact on satisfaction. Often these are overlooked features or such that are of no importance to customer decisions and satisfaction regardless of their presence or lack of
Reverse - covers product/feature expectations which when realised well will cause dissatisfaction with some customers, who may appreciate better simplicity
The Kano Matrix is used to easily plot the product features and have a discussions within the team about the correct category of a feature.
Look at Kano Model
Links we love
Check out these great links which can help you dive a little deeper into running the Kano Model practice with your team, customers or stakeholders.